Top 9 Symptoms of Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis is mainly caused by viruses of the flavivirus group, which can affect both humans and animals. The virus is transmitted from animals to ... read more...humans through mosquito bites. Animals that carry Japanese encephalitis are usually pigs and wild birds. Mosquitoes become infected with the virus after sucking blood from infected animals. The risk of an annual outbreak of Japanese encephalitis is usually highest during and after the rainy season. For this disease, any age can be infected if there is no specific immunity to the virus that causes the disease. Let's find out some symptoms of Japanese Encephalitis.
-
Japanese encephalitis is caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). It is spread by mosquito bites and is more common in areas of increased mosquito activity. It is endemic to parts of Asia and the Torres Strait region of Australia. Symptoms of encephalitis are often quite dangerous due to the potential for brain damage, severe neurological sequelae and a high mortality rate. The disease usually has a sudden onset with the first obvious symptom being a fever as high as 39-40 degrees Celsius.
Depending on the stage of the disease, each person will have different symptoms of encephalitis. Some people have a high fever, some people only have a mild fever, but there are also people with encephalitis without fever. The subjects most susceptible to encephalitis are young children because their resistance is still weak, and their immune systems are not yet complete, so they are easily attacked by viruses. Usually, the patient will have no fever in about 5 to 10 days if detected at the right time. On the contrary, if you ignore the symptoms and let them last, the disease is easy to recur, and the fever lasts or goes away on its own. The fever then returns gradually leading to chronic encephalitis. If you believe you may have Japanese encephalitis virus, seek emergency medical help.

medicalnewstoday.com 
medicalnewstoday.com -
Japanese encephalitis is an extremely dangerous disease and summer is the most likely time for outbreaks to become epidemic. Inflammation of the meninges can cause adverse effects on the nervous system, especially the brain and spinal cord. Patients may experience persistent high fever and persistent headaches. Japanese encephalitis has an incubation period of 5-14 days, with an average of about 1 week. In this stage, the patient has no obvious symptoms of the disease.
After the incubation period, the encephalitis virus will begin to attack the blood vessels of the brain, causing brain swelling and headaches. Headaches can occur suddenly on one-half or both sides of the head, leaving you in a state of fatigue and lack of vitality. This condition can come on suddenly and go away quickly but often repeats, so you should not be subjective but need to monitor them. Please visit your doctor for a timely medical examination. After performing diagnostic methods and making affirmative conclusions about Japanese encephalitis, the patient was hospitalized for treatment and regular monitoring.

medlatec.vn 
medlatec.vn -
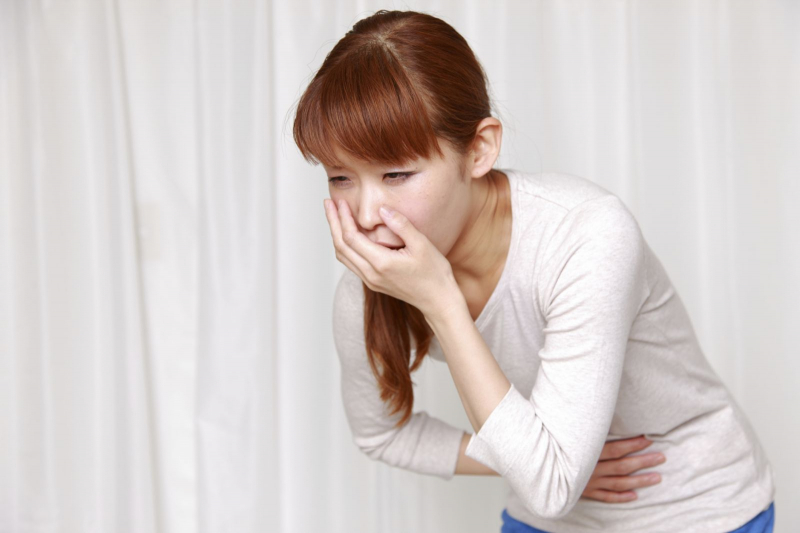
Japanese Encephalitis is an acute infectious disease that causes serious central nervous system infections in children and adults. After the incubation period, the Japanese encephalitis virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and causes danger signs. Initially, the patient's body showed symptoms of vomiting and nausea, headache. When nausea and loss of appetite, the human body can be accompanied by other symptoms such as vomiting, fever, headache, dizziness, belching, dry mouth, abdominal pain, and feeling tired. In more severe cases, other more serious symptoms may appear, such as shortness of breath with chest pain, and excessive sweating, which can lead to fainting.
For young children, due to their weak immune system, they often cry or cry intermittently, have diarrhea, may show signs of photophobia, lying in the trigger position. Prolonged vomiting is harmful to the body, can reduce physical energy levels, cause weight loss and affect psychological well-being. The disease is very dangerous, progresses rapidly within 24 hours if not treated aggressively. The disease is transmitted through the respiratory tract, so the possibility of infection when coming into contact with sick people is very high and the risk of developing an outbreak is very large if no timely control measures are taken.

medlatec.vn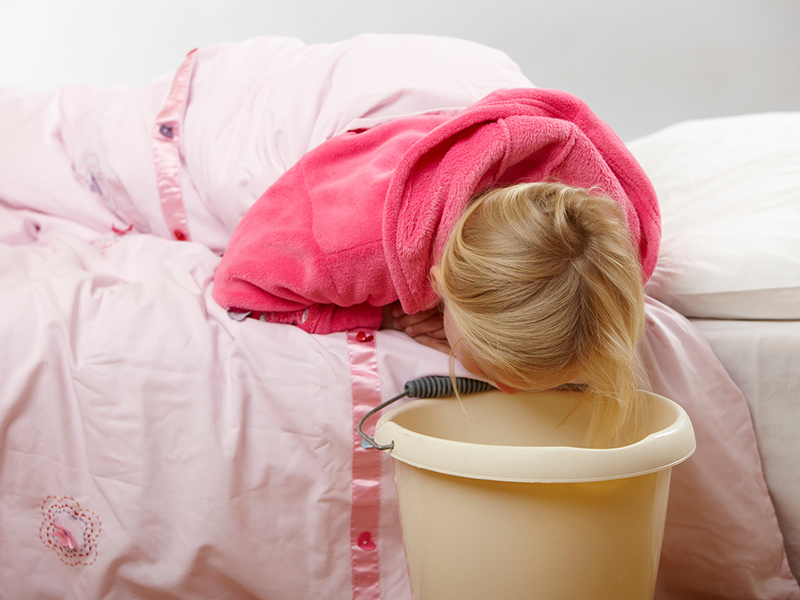 
medlatec.vn -
Japanese encephalitis is a dangerous disease that can leave sequelae. Because the initial manifestations of the disease are relatively similar to many other diseases, it is easy to confuse them with other fever-causing diseases, leading to late treatment. If the disease is detected late and is not treated in time, the disease can lead to many serious sequels such as cerebral palsy, leg paralysis, arm paralysis, epilepsy, etc. Encephalitis causes neurological complications, so when patients present with different manifestations.
Initially, the patient will have mild symptoms of numbness, tingling or decreased sensation. These symptoms then worsen and can lead to loss of sensation and paralysis. Paralysis can spread to many body parts such as arms, legs, and thighs leading to temporary or permanent loss of the ability to walk. When encephalitis is suspected, the patient should be taken to the nearest medical facility as soon as possible because the effectiveness of treatment depends largely on early detection and timely treatment. However, even when patients are diagnosed early and treated appropriately, there is an inevitable 5% to 10% death rate, usually within 24 to 48 hours of symptom onset.

medicalnewstoday.com 
medicalnewstoday.com -
In most cases, Japanese encephalitis in the first 3 to 5 days usually has insidious and nonspecific symptoms such as fever, malaise, and vomiting. However, meningitis can have a rapid onset and can be sudden in onset, making meningitis one of the few conditions in which otherwise healthy young people can fall into a coma with mild symptoms. and couldn't wake up.
When the patient is in a coma, their eyes are always closed and do not respond to light, do not respond to external stimuli, and do not breathe regularly. In other words, the patient loses the ability to awaken. In addition, the patient cannot speak and cannot understand what others say, and does not move with direction. When a coma occurs, the patient needs to be treated promptly otherwise there is a high risk of death. Therefore, patients need timely intervention by doctors to avoid leading to the worst outcome.
medicalnewstoday.com 
medicalnewstoday.com -
Japanese Encephalitis is a dangerous infectious disease caused by many viruses, often causing brain damage, neurological sequelae and high mortality. In the early stages, many hypothyroid patients complain of mental "darkness" and difficulty concentrating. Patients often experience strong hallucinations when looking at objects around them. The way this mental ambiguity manifests itself varies from person to person.
In the next stage, the patient falls into a state of delirium, and disorientation. Disorientation is caused by abnormal brain function that is sudden and goes away within days or weeks. However, this condition leads to intellectual decline, diffuse brain impairment, bilateral damage, or multifocal damage that reduces the memory storage area in the cerebral hemisphere. Japanese encephalitis is likely to leave severe sequelae with a rate of about 50%. The mortality rate of encephalitis is very high, averaging from 20% to 80% in patients with sequelae. So, when the body shows bad signs, go to the doctor right away.

vinmec.com 
vinmec.com -
Japanese Encephalitis is a very dangerous disease, especially in infants and young children. In the first 1-2 days of the disease, stiff neck, increased muscle tone, eyeball movement disorders, confusion or loss of consciousness, increased tendon reflexes, and obvious vasodilatation were observed. The manifestations of nerve damage in children are increasingly severe, easily producing hallucinations, agitation, seizures, and contractions. When the disease progresses in severe form, there will be stiff or vibrating convulsions in the face and extremities leading to paralysis, and spastic paralysis in a certain position.
During the seizure, the patient remains awake and is characterized by clenched fists, flexed back and arms in a flexed or flexed position, with legs extended. The convulsion lasts a few seconds to a few minutes or more. When having a seizure, patients are very susceptible to laryngospasm, and respiratory muscle spasms leading to hypoventilation, hypoxia, cyanosis, apnea and possibly death. This is the stage when the virus attacks the brain, and occurs very quickly because there is no longer a protective barrier, causing the nervous system to be destroyed, so most children can die within the first 7 days of illness. However, children who pass this stage have a very high cure rate.

marrybaby.vn 
marrybaby.vn -
Most people with Japanese encephalitis do not have any symptoms. Some people may experience symptoms of tremors. A tremor is a rhythmic, involuntary movement of muscle groups, usually occurring in the hands, feet, head, face, vocal cords, or trunk. Depending on the severity of the disease, each person has a different type of tremor. The first type is static tremors, usually occurring when an organ is resting. Examples include tremors in the legs at rest, tremors in the arms at rest, tremors localized in the chin, and tremors in the vocal cords. Many people mistake static tremors for symptoms of Parkinson's disease, so they don't see a doctor.
The second type is postural tremors, which is a tremor when the patient holds the arm or leg in a particular position for a certain period of time, for example, tremor when standing, tremor when straightening. Postural tremor suggests a cause for essential tremor or physiological tremor if the onset of the tremor is progressive. In addition, postural tremors may be seen in toxic or metabolic diseases if their onset is abrupt.
The third type is essential tremors, which is common in the elderly, without underlying medical causes. Essential tremor rarely occurs without the use of the hand but is more pronounced when trying to perform an action, such as while writing or reaching for something. When you see unusual symptoms in your body, go to the nearest medical facility for a medical examination to avoid serious complications.
hellodoctors.vn 
hellodoctors.vn -
Neck stiffness is one of the most popular symptoms of Japanese Encephalitis. The disease causes inflammation in the spine and spinal cord by viruses and bacteria, causing neck pain that cannot be rotated. At first, the hospital will have pain in the neck area, the pain is increasing. The disease is caused by inflammatory nodules in the joints, causing the joint area between the cervical vertebrae to enlarge, compressing the nerves and spinal cord. This painful symptom is often accompanied by muscle tension, so movement is limited, neck rotation is painful.
The mucinous nucleus inside the disc leaks out through the opening of the torn capsule, entering the spinal canal, causing the surrounding nerves to be compressed and causing stiff neck pain. It begins with a stiff neck, followed by a headache, or the pain may radiate down the shoulder, arm, and hand. In some cases, Japanese encephalitis may be confused with lying in the wrong position, causing the neck to become stiff. When experiencing this symptom, the patient can alternate hot compresses with a moderate heating pad, or by taking a warm bath to relieve stiff neck pain. Then, go to the hospital to be thoroughly treated for Japanese encephalitis.

microspinemd.com 
microspinemd.com