Top 11 Symptoms of Typhoid Fever
The S. Typhi bacterium causes the sickness known as typhoid fever. It results in diarrhea, a high fever, and flu-like symptoms. Even if you don't feel ill, ... read more...typhoid can make you contagious. Antibiotics should be taken as soon as possible to treat typhoid because it can be fatal. You should get vaccinated if you reside in or plan to visit a region where typhoid is widespread. To understand more about this illness, read this list of symptoms of Typhoid fever and seek medical help if you have some of these symptoms.
-
Many people experience headaches, which practically everyone does. In 2020, experts predicted that 50 to 75 percent of adults would experience headaches. Most headaches are brief and moderate, but some can be incapacitating and interfere with your everyday activities.
An estimated 3 billion individuals worldwide experience primary headaches each year, including migraine and tension headaches, which are among the most frequent headaches for which people seek medical attention. Typhoid fever is one of several illnesses and ailments that can result in a headache. You may find out more about headaches, such as migraine headaches, and the therapies that can improve your quality of life.
It could be necessary to consult a doctor if you get headache symptoms three or more times each month. If the headaches affect your quality of life or lead to further issues like stress, sadness, or other worries, you might also want to think about getting preventative treatment.

Photo by Gerd Altmann via Pixabay 
Photo by Lukas Bieri Lukas Bieri via Pixabay -
Typhoid is a food and waterborne disease endemic to many countries. In order to avoid catching typhoid, practice food and water safety and get vaccinated before entering a risk area. Although the disease can be effectively prevented by the vaccine, there is still a slight chance of infection, therefore you should be able to recognize the signs.
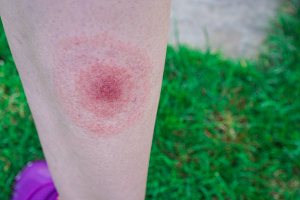
A rash of flat, rose-colored patches might appear on certain patients who have typhoid fever or paratyphoid fever. Rose-colored patches (arrows) develop on the chest and abdomen in around 10 to 20% of typhoid fever patients, typically during the second week of infection. According to some studies, rose spots are clumps of bacteria that travel via the bloodstream as bacterial emboli to the skin.The majority of Americans with typhoid or paratyphoid fever develop the illness when traveling overseas, most frequently to nations where these illnesses are prevalent, where the water and food may be contaminated, and where sanitation is subpar. Travelers should take steps to avoid infection when visiting South Asia, particularly Pakistan, India, and Bangladesh. In East Asia, Africa, the Caribbean, Central, and South America, typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever are somewhat less prevalent. In the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and Japan, both diseases are quite uncommon. Get vaccinated against typhoid fever if you intend to travel outside of the United States.
Owner: Medical Symptom Information via Youtube 
Photo by mohamed_hassan via Pixabay -
The symptoms of typhoid fever usually develop 1 or 2 weeks after a person becomes infected with the Salmonella typhi bacteria. With treatment, the symptoms of typhoid fever should quickly improve within 3 to 5 days. Typhoid fever often worsens over a few weeks if untreated, and there is a high likelihood that it may lead to potentially fatal complications.
One of the first indications of typhoid fever is a cough. Within 3 to 4 weeks, a cough will typically go away on its own.
When you have a cough, you typically don't need to visit the doctor. Instead, if your temperature is high or you don't feel well enough to carry out your usual activities, you should get enough rest, drink a lot of fluids, try to stay at home, and avoid interaction with other people. To relieve any pain, you might also try using ibuprofen or paracetamol, as well as hot lemon and honey (not suitable for babies under 1 year old). However, there is little proof that they are effective. Cough suppressants and hot lemon and honey are comparable in effectiveness.

Photo by Tumisu via Pixabay 
Photo by Annie Spratt via Unplash -
The word "fatigue" refers to an all-encompassing sense of exhaustion or lack of energy. Being sleepy or drowsy is not the same thing as being groggy. You lack motivation and energy when you're worn out. The two things are not the same, even if being drowsy may be a sign of exhaustion. Many different medical disorders, from mild to severe, can all cause fatigue, which is a typical symptom. Additionally, some lifestyle decisions—like inactivity or a bad diet—can naturally lead to it.
Consult your doctor if your weariness doesn't go away with adequate rest and nourishment or if you think it might be brought on by a physical or mental health condition. They can work with you to identify the root of your exhaustion and address it. Your doctor can request some tests if they think you have an underlying medical disease that is the root of your fatigue. They might, for instance, request blood or urine tests.

Photo by Concord90 via Pixabay 
Photo by mohamed via Pixabay -
When you have diarrhea, you usually have loose, watery stools and feel the urgent need to go to the bathroom several times per day. You can have acute or persistent diarrhea. When diarrhea persists for 1–2 days, it is considered acute. Typhoid fever could be brought on by a viral or bacterial illness that you ingested or drank. When you have diarrhea most days of the week for more than three to four weeks, you have chronic diarrhea. You must consume extra water or liquids that replace electrolytes, including sports drinks. The majority of acute diarrhea episodes resolve on their own, and symptoms usually go better in a couple of days.
However, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases advises seeking medical attention if symptoms last for more than two days since you might be dehydrating and require IV fluids or other treatment and evaluation. If your child is having diarrheal symptoms, get medical help right away.
Photo by Clker-Free-Vector-Images via Pixabay 
Photo by Giorgio Trovato via Unplash -
Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever have similar symptoms. People usually have a sustained fever that can be as high as 103–104°F (39–40°C). A sustained fever is a fever that does not come and go. If you have a fever and feel very ill, see a doctor immediately. Patients who do not receive the proper antibiotic treatment may experience a fever for weeks or months and may also experience other health issues. These medical conditions can cause people to pass away if they are not treated.
You can still be carrying Salmonella Typhi or Salmonella Paratyphi even if your symptoms seem to go away. If so, you run the risk of getting sick again or spreading the infection to other people. Some people might not be able to go back to work until a medical professional certifies that they are free of the bacterium. These individuals consist of caregivers, healthcare professionals, and food handlers.
These actions can reduce the risk of spreading the bacterium to someone else if you are receiving treatment for typhoid fever: Continue taking antibiotics as long as your doctor has instructed you to, After using the restroom, gently wash your hands with soap and water. Avoid preparing or serving food to others.
Photo by Polina Tankilevitch via Pexels 
Photo by Anna Shvets via Pexels -
Typhoid fever symptoms often develop 1-2 weeks after the infectious disease. Body aches and pains could affect the patient. The first week of an illness is when this symptom typically emerges. Together with a high temperature that doesn't go down, muscle pains are another typical sign of typhoid fever. The likelihood of getting the sickness increases as a patient's signs and risk factors increase. Yet a blood test for typhoid antibodies is required to determine whether you are experiencing a typhoid fever or not.

Photo by Victor Freitas via Pexels 
Photo by Scott Webb via Pexels -
Typhoid fever patients have bacteria in their blood and intestines. This intestinal infection is typically brought on by Salmonella typhi bacteria. Symptoms include prolonged high fever, fatigue, headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhea. Typhoid fever symptoms include vomiting, which the body uses to get rid of dangerous things from the stomach or as a reaction to something else.

Photo by 愚木混株 Cdd20 via Pixabay 
Photo by Clker-Free-Vector-Images via Pixabay -
The early symptoms of typhoid fever include chills, sweating, a dry cough, headache, body aches, and abdominal pain. As chill feelings occur, a high and recurring fever may then develop. You may get either diarrhea or vomiting. There are cases where individuals who recover from typhoid fever still contain the bacteria in their stool without becoming ill. They're called Carriers. They can spread the virus to other people.

Photo by OpenClipart-Vectors via Pixabay 
Photo by freepik -
Loss of appetite is one of the common signs of typhoid fever. A medical problem is frequently the cause of appetite loss, in this case, typhoid fever causes you to lack appetite. As the infection progresses, you may lose your appetite, feel sick, and have a tummy ache and diarrhoea. If you observe a dramatic loss in your appetite, consult your doctor. In theory, any medical condition could cause loss of appetite.

Photo by Andres Ayrton via Pexels 
Photo by Mikhail Nilov via Pexels -
Typhoid fever can cause cells in the walls of the small intestine or large bowel to die off. This enables the gut's contents to enter the body. It may result in sepsis, an infection that affects the entire body and causes serious abdominal pains, vomiting, and diarrhea.
If you reside in an area where typhoid fever is widespread, you can get a vaccination against typhoid fever. Access to purified water helps people avoid coming into touch with the Salmonella enterica serotype typhi bacteria in areas where typhoid illness is endemic. Managing human waste also aids in protecting humans from microorganisms. Also, it's crucial for those who make and serve meals to wash their hands thoroughly.
Photo by Christian Dorn via Pixabay 
Photo by Andrea Piacquadio via Pexels