Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant
Bone marrow is composed of soft tissue, blood vessels, and capillaries and is found in the center of many bones. The primary function of bone marrow is to produce blood cells that aid in the maintenance of a healthy vascular and lymphatic system, with over 200 billion cells produced each day. Both red and white blood cells are produced by the bone marrow. The constant production and regeneration of these cells is critical in aiding the body's fight against disease and infection, as well as in keeping the respiratory system operational.
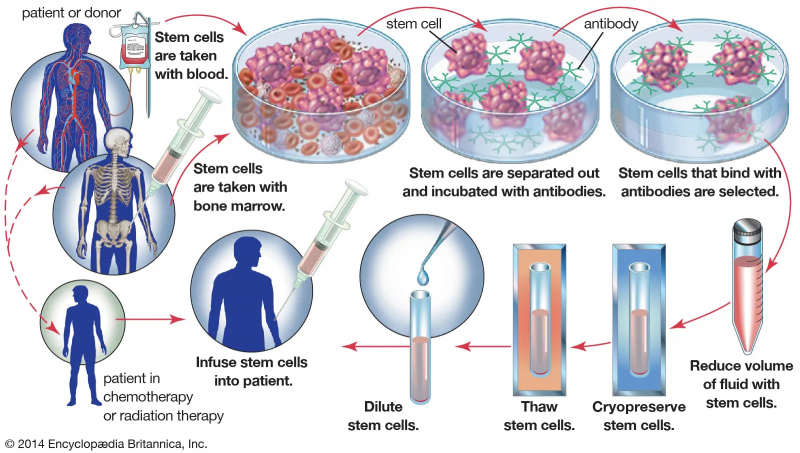
A variety of medical conditions, including leukemias and cancers, tuberculosis, and sickle cell anemia, can impair bone marrow production. Diseases affecting the bone marrow can be fatal if left untreated. The first step in treating a bone marrow disease is the surgical removal of the affected bone marrow. This is analyzed to provide a diagnosis and to determine which treatment option is best. If cancerous cells are found, the most likely treatment will be chemotherapy or radiotherapy, with the goal of destroying the cancer cells and preventing them from spreading further. A number of red and white blood cells will be damaged as well. A bone marrow transplant is the most effective way to treat a bone marrow condition because it replaces damaged marrow and cells with new, healthy ones. Stem cells, which are early development cells capable of producing both red and white blood cells, are typically used in bone marrow transplants.
The stem cells are injected from donor blood marrow, which can come from an external donor or from within the patient. External donor stem cells must be a very close match to the patient's and are typically taken from the pelvic area. The donor stem cells are infused into the patient's bone via a vein using a drip infusion, which is a painless and minimally invasive procedure. Over the course of several hours, the donor material travels to the bone marrow. It will take 2 to 4 weeks for the implanted stem cells to begin producing new red and white blood cells, and the patient will need to remain isolated during this time due to the high risk of infection.
An allogeneic bone marrow transplant is a complex procedure that necessitates the expertise of experienced specialists and can thus be costly. Many people choose to seek treatment in another country, either to save money or to find specialized care.
Cost: $890,000