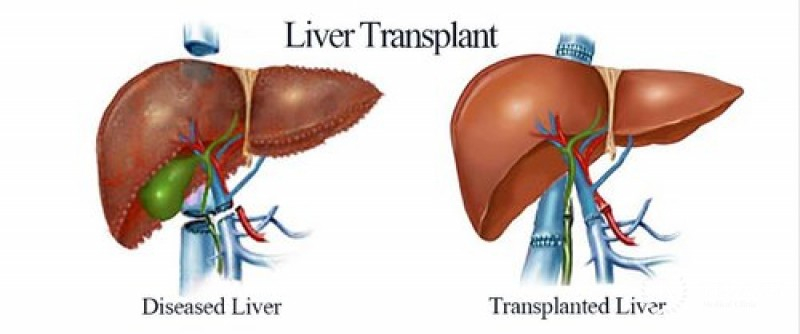
Liver Transplant
The replacement of a diseased liver with a healthy liver from another person is known as liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation (allograft). Although donor organ availability is a major limitation, liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, which involves removing the native liver and replacing it with the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver.
The surgical procedure is complicated, requiring meticulous harvesting of the donor organ and implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is strictly regulated and is only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and their support teams. Depending on the outcome, the surgery can last anywhere from 4 to 18 hours. A well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match, as well as careful screening for eligible recipients, are required for favorable outcomes.
Liver transplantation may be used to treat acute or chronic conditions that result in irreversible and severe ("end-stage") liver dysfunction. Because the procedure carries relatively high risks, is resource-intensive, and necessitates major life changes following surgery, it is reserved for emergency situations. Because outcomes are highly variable, judging the appropriateness/effectiveness of liver transplantation on a case-by-case basis is critical.
Cost: $812,500