Top 10 Best Foods High in Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral for good health. It is essential for the function of over 300 enzymes and is involved in a variety of important processes in your ... read more...body. It metabolizes nutrition, keeps your immune system in control, and grows and repairs body tissues. Because your body does not retain zinc, you must take enough every day to meet your daily requirements. Below are some Best Foods High in Zinc that you can refer to!
-
Zinc may be found mainly in meat. Red meat is a particularly good source, although other types of meat, including beef, lamb, and pork, contain significant amounts. A 100-gram (3.5-ounce) portion of raw ground beef provides 4.8 mg of zinc, which is 44% of the Daily Value (DV). 176 calories, 20 grams of protein, and 10 grams of fat are also provided by this amount of meat.
It also contains a lot of other critical minerals including iron, B vitamins, and creatine. It's worth mentioning that consuming a lot of red meat, particularly processed meat, has been related to an increased risk of heart disease and some cancers. However, as long as you control your intake of processed meats and consume unprocessed red meats as part of a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber, this is unlikely to be a problem.

Meat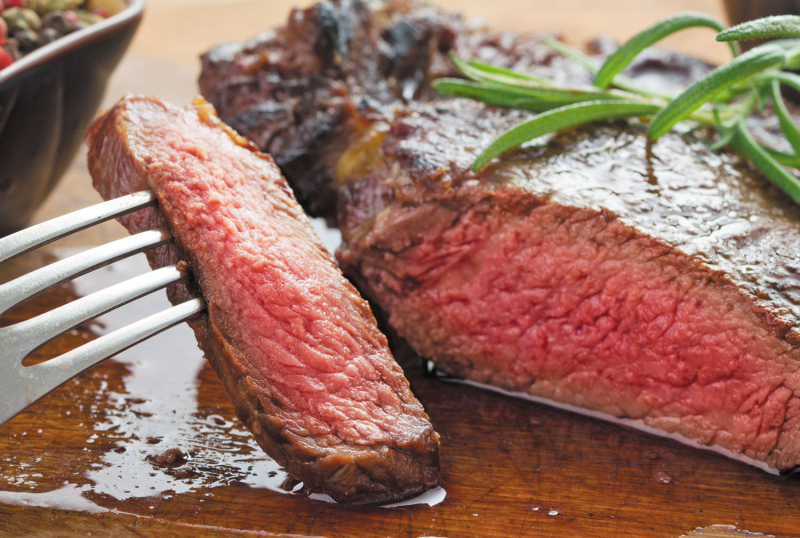 
Meat -
Zinc is found in the largest amounts in high-protein foods like meat and fish. Shellfish are a low-calorie, healthful source of zinc. Oysters have the highest zinc content of any food. They provide the highest concentration, with 6 medium oysters giving 32 mg or 291% of the daily requirement.
Other shellfish have a lower zinc concentration than oysters, but they are still good sources. Skate, anchovies, herring, sardines, crab, prawns, shrimps, mussels, and winkles are some examples. Alaskan crab, for instance, has 7.6 mg per 100 grams (3.5 ounces), or 69 % of the daily requirement. Shrimp and mussels, both of which contain 14% of the DV per 100 grams, are other good sources (3.5 ounces). If you are pregnant, however, ensure sure shellfish is properly cooked before eating it to avoid food poisoning.
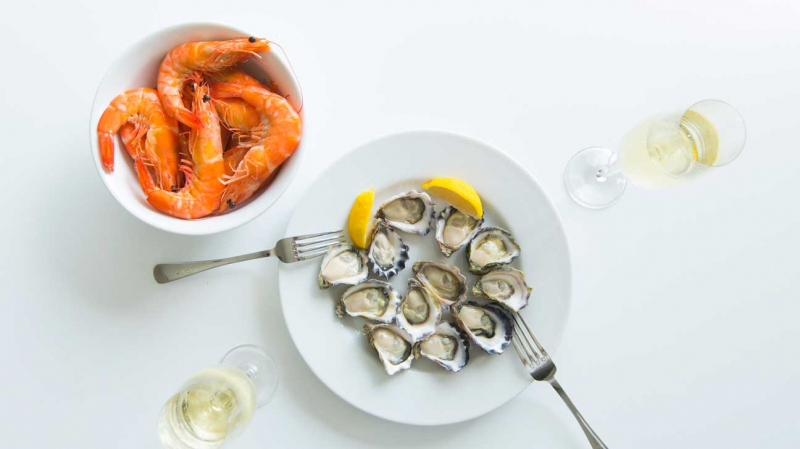

Shellfish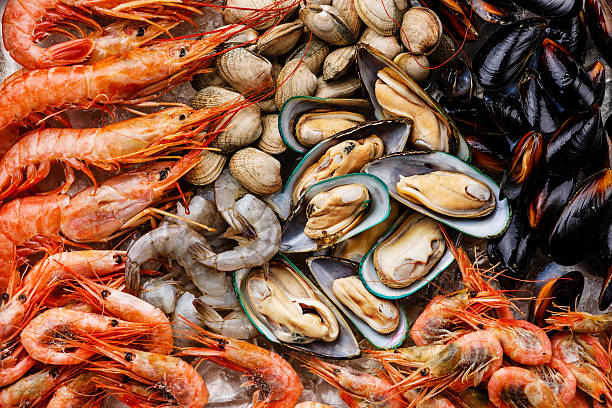 
Shellfish -
Lentils, beans, and chickpeas are high in protein as well as important vitamins and minerals such as zinc. In fact, 100 grams of cooked lentils provide around 12% of the daily value. Chickpeas provide 1.3 mg of zinc per half-cup, while kidney beans have 0.9 mg.
However, they also contain phytates. Antinutrients prevent zinc and other minerals from being absorbed, therefore zinc from legumes isn't as well absorbed as zinc from animal products. Phytates can be reduced by cooking, sprouting, or fermenting legumes, making it simpler for your body to absorb the mineral. They might be a good source of zinc for vegetarians and vegans. They're also high in protein and fiber, and they're easy to include in soups, stews, and salads.
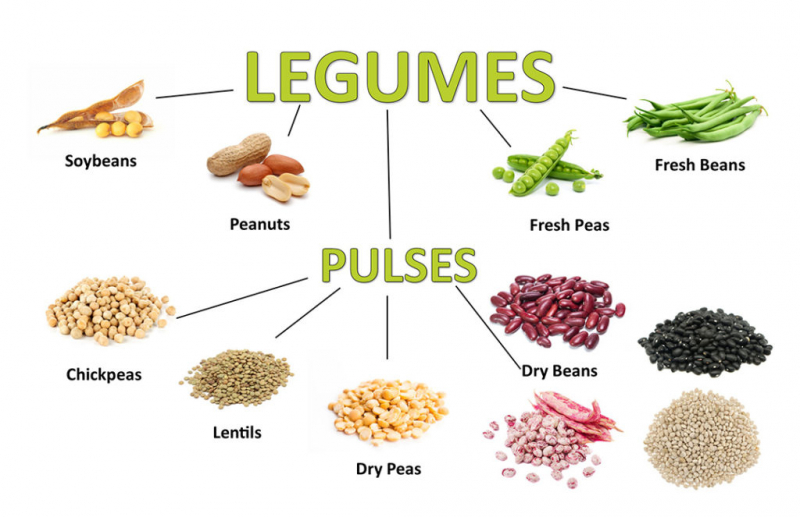
Legumes 
Legumes -
Seeds are a nutritious addition to your diet that can help you get more zinc. Some seeds, though, are better than others. 3 tablespoons (30 grams) of hemp seeds, for example, contain 31% and 43% of the daily recommended intake for men and women, respectively.
Squash, pumpkin, and sesame seeds are some of the other seeds that are high in zinc. Seeds are an excellent addition to your diet since they include fiber, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals in addition to zinc. They've also been linked to several health benefits, including lower cholesterol and blood pressure when consumed as part of a healthy diet. You may incorporate hemp, flax, pumpkin, or squash seeds into your diet by including them in salads, soups, yogurts, or other foods.
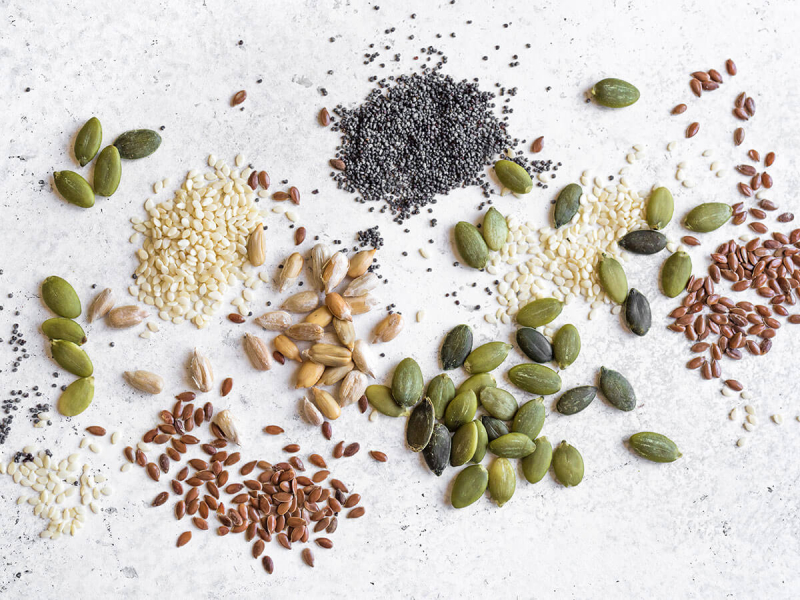

Seeds 
Seeds -
Zinc intake may be increased by eating pine nuts, peanuts, cashews, and almonds. Nuts also include a variety of other beneficial nutrients, such as healthy fats and fiber, as well as a variety of vitamins and minerals.
They can also supply different levels of zinc. Cashews are a good choice if you're looking for a zinc-rich nut. A 1-ounce portion of cashews, for example, has 1.6 mg, whereas a 1-ounce serving of dry-roasted almonds contains 0.9 mg. Nuts are also a quick and easy snack, and they've been linked to a lower risk of diseases including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. Furthermore, those who eat nuts live longer than those who do not, making nuts an excellent supplement to every diet.
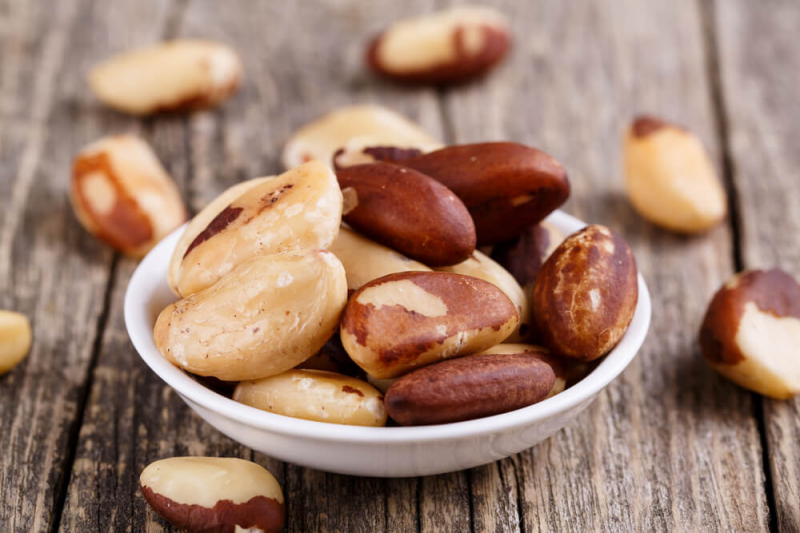

Nuts 
Nuts -
In Western diets, where dairy consumption is high, dairy products can provide a reasonable contribution to dietary zinc intake. Cheese and milk, for example, are high in zinc and other minerals.
Milk and cheese are two significant sources of bioavailable zinc, which means that the majority of the zinc in these foods can be absorbed by your body. 100 grams of cheddar cheese, for example, has roughly 28% of the daily value, whereas a single cup of full-fat milk contains about 9%. These foods also include a variety of other nutrients that are beneficial to bone health, such as protein, calcium, and vitamin D. The combination of cereals and legumes with dairy products is one way to boost zinc absorption from diets where zinc is poorly bioavailable.
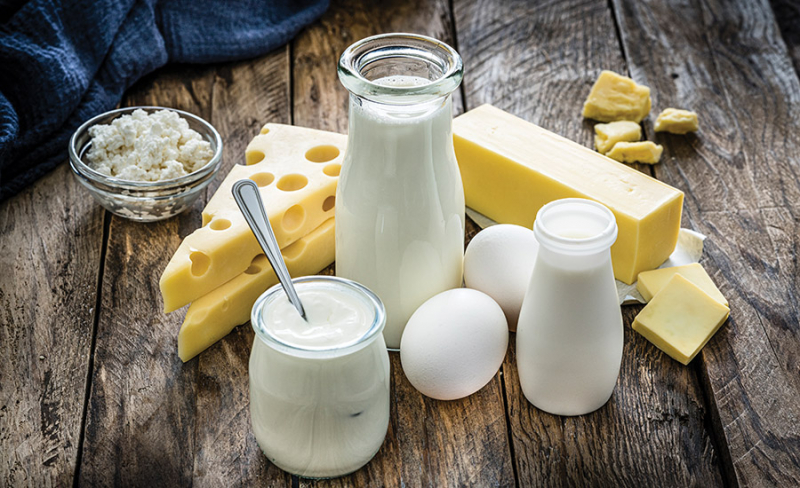

Dairy 
Dairy -
Eggs are a good source of zinc and can help you meet your daily requirements. One big egg, for example, contains around 5% of the daily value. This contains 77 calories, 6 grams of protein, 5 grams of healthy fats, as well as a variety of vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins and selenium. Whole eggs are also a good source of choline, which is a nutrient that most people don't get enough of.
However, zinc is not much in eggs. To receive the zinc your body requires, you'd have to consume at least a dozen eggs every day, which isn't healthy for your health. If you enjoy eggs, you can continue to consume them in moderation to meet part of your daily zinc needs. Other sources of zinc should be included in your diet for a well-balanced diet. You may meet your daily nutritional demands by eating a wide variety of foods. Oysters, crab, lobster, beef, chicken, yogurt, cashews, and chickpeas are all rich sources of zinc.

Eggs 
Eggs -
Zinc is found in whole grains such as wheat, quinoa, rice, and oats. Grains, like legumes, contain phytates, which bind to zinc and prevent it from being absorbed. Whole grains have higher phytates than refined grains, which means they will offer less zinc.
However, they are far healthier for your health and include numerous essential nutrients such as fiber, B vitamins, magnesium, iron, phosphorus, manganese, and selenium. Unlike refined grains, which are stripped of valuable nutrients during the refining process, whole grains provide a "complete package" of health benefits. In fact, consuming whole grains has been linked to a longer lifespan as well as a variety of other health benefits, such as a reduced risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.

Whole Grains 
Whole Grains -
Fruits and vegetables, in general, are low in zinc. Some veggies, on the other hand, contain reasonable quantities and can help you meet your daily requirements, especially if you don't eat meat.
Because zinc is not as bioavailable in plant foods as it is in animal foods, vegans and vegetarians who eat mostly plant foods may have difficulty getting enough zinc. Shiitake mushrooms, green peas, spinach, lima beans, lentil sprouts, asparagus, beet greens, broccoli, okra, and sweet corn are all high in zinc that you can refer to add to your diet. Potatoes, both regular and sweet varieties, contain around 1 mg per large potato, or about 9% of the daily requirement. Green beans and kale, for example, have just around 3% of the daily value per 100 grams. Even though vegetables are low in zinc, they have been associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases including heart disease and cancer.

Some Vegetables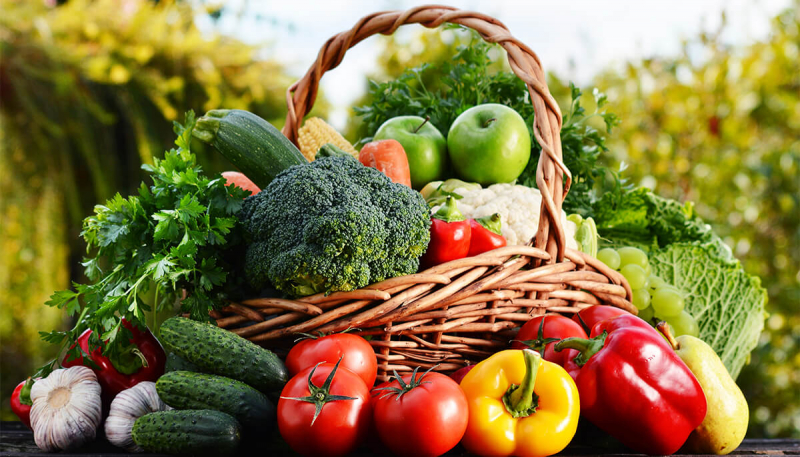 
Some Vegetables -
Dark chocolate, maybe surprisingly, has a reasonable amount of zinc. Chocolate ingredients may help decrease your risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and diabetes when consumed in moderation, however, further research is needed to confirm these benefits. Dark chocolate is the healthiest variety of chocolate because it includes more nutrients than milk or white chocolate, including copper, iron, and zinc.
A 100-gram (3.5-ounce) bar of 70%–85% dark chocolate provides 3.3 milligrams of zinc or 30% of the daily value. Dark chocolate, on the other hand, has 600 calories per 100 grams. While it contains certain beneficial nutrients, it is also a high-calorie food. While your treat may provide some extra nutrients, it is not a food you should rely on as your main source of zinc.
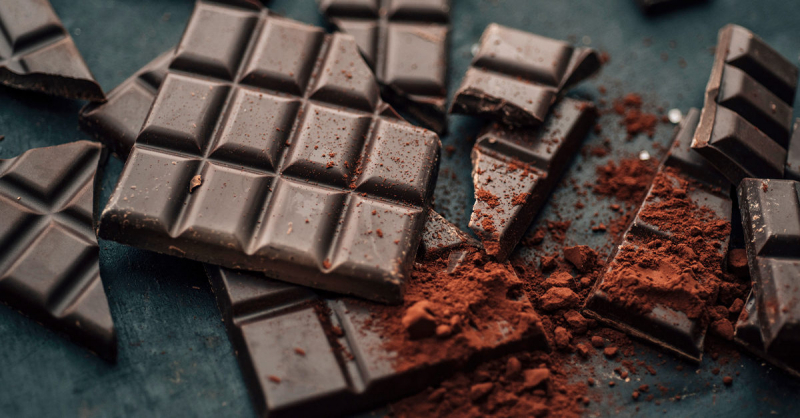

Dark Chocolate 
Dark Chocolate































