Top 10 Natural Ways to Increase Your Glutathione Levels
Glutathione is an essential antioxidant that is mostly produced by the body but can also be received through food. Unfortunately, aging, a bad diet, and a ... read more...sedentary lifestyle can all cause your levels of this antioxidant to decrease. Fortunately, there are some ways to increase your glutathione levels. Read on for more information!
-
In some plant and protein-based foods, sulfur is an essential mineral that occurs naturally. Important proteins and enzymes in the body need it for their structure and function. Notably, glutathione can only be made with sulfur.
Methionine and cysteine are two amino acids that contain sulfur in food. It primarily comes from dietary sources of proteins such as beef, fish, and poultry. The cruciferous vegetable broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, kale, watercress, and mustard greens are among vegetarian sources of sulfur. Studies on both humans and animals have found that eating plants high in sulfur may lessen oxidative stress by raising glutathione levels. Additionally, allium foods such as garlic, shallots, and onions increase glutathione levels, possibly due to the sulfur-containing compounds they contain.

Consume Sulfur-Rich Foods 
Consume Sulfur-Rich Foods -
Water-soluble vitamin C is present in many foods, especially fruits and vegetables. Foods high in vitamin C include strawberries, citrus fruits, papayas, kiwis, and bell peppers.
This vitamin has a variety of purposes, one of which is functioning as an antioxidant to protect cells from oxidative damage. Additionally, it maintains the body's supply of glutathione and other antioxidants. Vitamin C may help raise glutathione levels by sparing glutathione by attacking free radicals first, thereby sparing glutathione. Additionally, they found that vitamin C promotes glutathione processing by converting oxidized glutathione to its active form. In fact, studies have shown that healthy adults who take vitamin C supplements have higher glutathione levels in their white blood cells. One study found that when adults took 500–1,000 mg of vitamin C daily for 13 weeks, the amount of glutathione in their white blood cells increased by 18%. Another study showed that supplementing with 500 mg of vitamin C daily raised glutathione in red blood cells by 47%. But in these investigations, vitamin C supplements were used. It's uncertain if foods would have the same effect as supplements, which are concentrated versions of the vitamin.
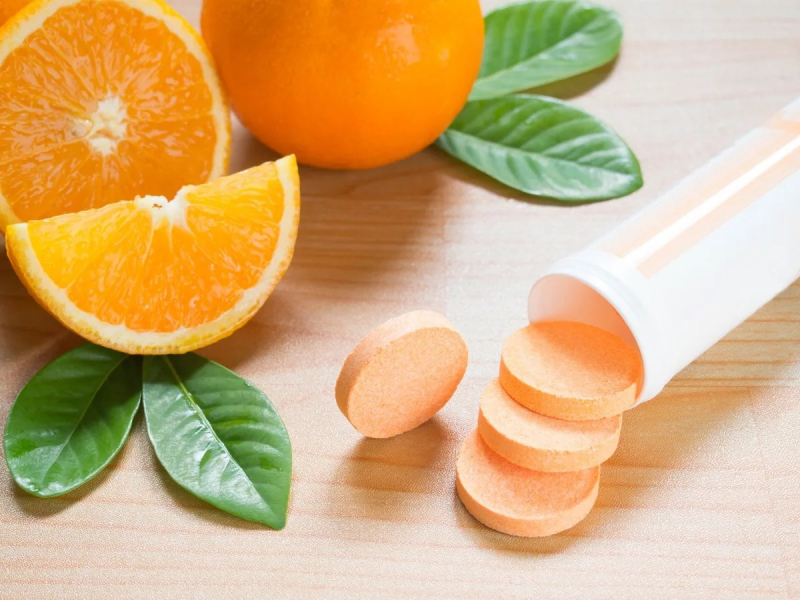

Increase Your Vitamin C Intake 
Increase Your Vitamin C Intake -
Selenium is a necessary mineral and a cofactor for glutathione, which means it is a substance required for glutathione activity. The best sources of selenium include organ meats, beef, chicken, fish, cottage cheese, brown rice, and Brazil nuts.
You may be able to increase or maintain your body's production of glutathione by increasing your selenium intake. For adults, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for selenium is 55 mcg. This is based on the quantity required to maximize the production of glutathione peroxidase. In one study, 45 patients with chronic kidney disease were examined to determine the effects of selenium supplementation. For three months, each of them received 200 mcg of selenium daily. It's worth noting that all of their glutathione peroxidase levels dramatically increased. Another study found that patients receiving hemodialysis had higher levels of glutathione peroxidase after taking selenium supplements. Once more, the studies mentioned above focused on supplements rather than foods high in selenium.

Add Selenium-Rich Foods to Your Diet 
Add Selenium-Rich Foods to Your Diet -
Glutathione is produced by the human body, but it can also be received through food. Among the richest food sources include okra, avocados, asparagus, and spinach.
However, the body has trouble absorbing dietary glutathione. The amount of glutathione in food can also be decreased by cooking and storage conditions. Foods high in glutathione may lessen oxidative stress even though they have a less significant influence on raising glutathione levels. For instance, a non-experimental investigation revealed that mouth cancer risk was reduced in those who ate the most foods high in glutathione. To fully understand the impact of foods high in glutathione on oxidative stress and glutathione levels, more research is necessary.

Eat Foods Naturally Rich in Glutathione 
Eat Foods Naturally Rich in Glutathione -
Certain amino acids are required for the synthesis of glutathione in your body. In the synthesis of glutathione, the amino acid cysteine plays a particularly significant role.
Cysteine-rich foods, including whey protein, can help you produce more glutathione. It's widely known that whey protein builds muscles, but one of the most under-appreciated benefits of daily supplementation of whey protein is that it increases your body’s levels of glutathione. In fact, the evidence clearly backs up this claim, with numerous studies finding that whey protein may raise glutathione levels and thereby reduce oxidative stress. In a study from 2012, scientists found that whey protein reduced oxidative stress in human colon cancer cells, which they believed was made possible by the protein's increase in glutathione levels.

Supplement With Whey Protein 
Supplement With Whey Protein -
Supplements made from milk thistle are another natural way to raise glutathione levels. This herbal supplement is made from the milk thistle plant (Silybum marianum).
Three active substances, together known as silymarin, make up milk thistle. Silymarin, which is well known for its antioxidant properties, is present in milk thistle extract in high proportions. Additionally, silymarin has been demonstrated in rodent and test-tube tests to raise glutathione levels and prevent depletion. According to research, silymarin keeps glutathione levels stable by preventing cell damage. Before consuming any milk thistle extract, consult your physician to rule out any potential side effects or contraindications based on your specific health situation.

Consider Milk Thistle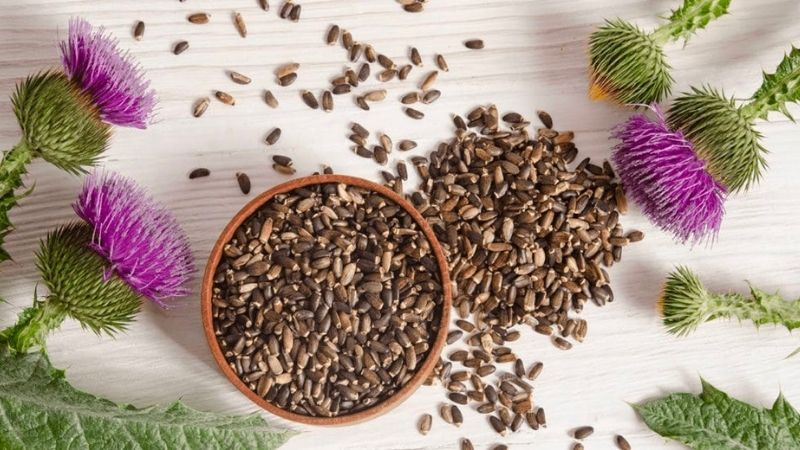 
Consider Milk Thistle -
Indian cuisine loves the vibrant yellow-orange plant and spice known as turmeric. Since ancient times, India has used the herb for medical purposes. Curcumin, turmeric's main component, is probably responsible for its therapeutic effects.
When compared to the spice, the curcumin content of turmeric is much more concentrated in the extract form. The ability of turmeric and curcumin extract to raise glutathione levels has been demonstrated in numerous animal and test-tube studies. Researchers have shown that the curcumin in turmeric may help restore healthy levels of glutathione and improve the activity of glutathione enzymes. It would be very challenging to consume the same levels of curcumin with turmeric spice, therefore if you wanted to experience a boost in glutathione levels, you would need to take turmeric extract.
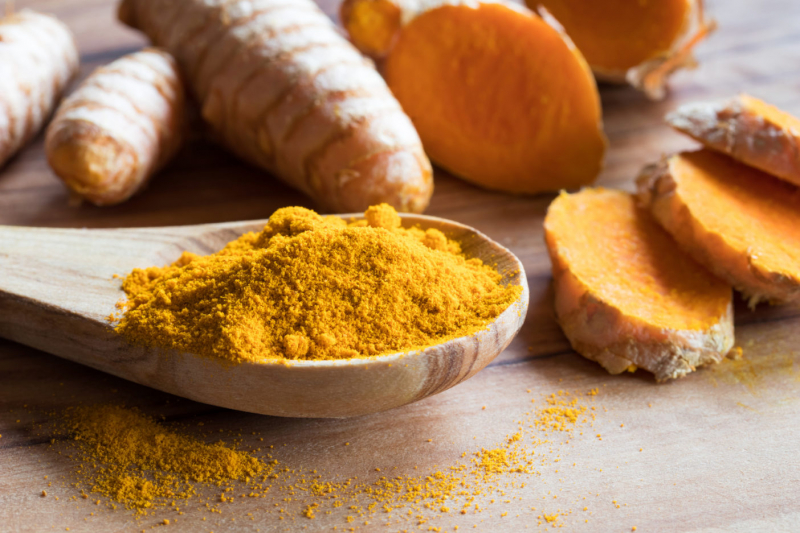

Try Turmeric Extract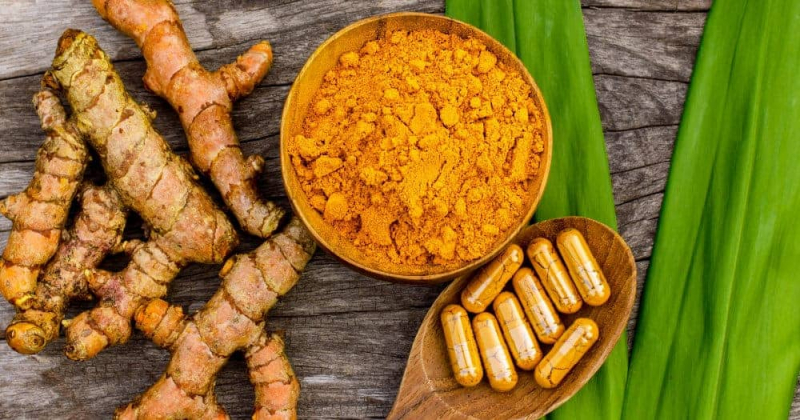 
Try Turmeric Extract -
Beyond food, the way you live is an equally important factor in how your body produces and uses glutathione. A restful night's sleep is crucial for overall health. so make sure to get enough sleep, generally at least 7.5 hours each night.
It's worth noting that chronic sleep deprivation can lead to oxidative stress and even hormone imbalances. Additionally, research has shown that chronic sleep deprivation may lower glutathione levels. For instance, glutathione peroxidase activity was much lower in those with insomnia, according to a study that examined glutathione levels in 30 healthy adults and 30 people with insomnia. Numerous research on animals has demonstrated that lack of sleep lowers glutathione levels. To maintain or increase your levels of this antioxidant, make sure you get good, restorative sleep every night.

Get Enough Sleep 
Get Enough Sleep -
For a very long time, physicians and other healthcare professionals have advised regular physical activity. It should come as no surprise that exercise is beneficial for both physical and mental health.
Recent studies have demonstrated that exercise helps to maintain or raise antioxidant levels, particularly glutathione. Compared to doing cardio or weight training alone, doing both cardio and circuit weight training improves glutathione levels the highest. The risk of decreased glutathione production arises in athletes who overtrain without maintaining proper nutrition and rest. As a result, make sure to gradually and wisely add physical exercise to your daily schedule. Schedule (and do) exercise for 30 minutes each day, which can be part of your daily routine, such as walking or biking to work.

Exercise Regularly 
Exercise Regularly -
It should come as no surprise that excessive and regular alcohol consumption has a number of negative health impacts. Excessive alcohol intake is the third-leading cause of preventable death in the United States.
Ailments like liver cirrhosis, brain damage, and pancreatitis are frequently linked to alcoholism. Lung damage is a side effect of drinking that is less well-known. This most likely has something to do with the lungs' glutathione levels being low. Glutathione is necessary for the normal functioning of the lungs' small airways. In fact, healthy lungs contain up to 1,000 times as much glutathione as other human organs. Most likely, the oxidative stress brought on by long-term alcohol consumption is what causes glutathione to be reduced in the lungs of alcoholics. Do not drink alcohol, or limit yourself to one drink once or twice per week.

Avoid Drinking Too Much Alcohol 
Avoid Drinking Too Much Alcohol