Top 10 Simple Tips to Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes
When your blood sugar increases and then drops quickly after you eat, this is known as a blood sugar spike. Over time, your body may be unable to efficiently ... read more...control blood sugar, leading to type 2 diabetes. Blood sugar increases can harden and narrow your blood vessels, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Below are some of the Simple Tips to Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes you can refer to!
-
Blood sugar rises as a result of carbohydrates (carbs). Carbs are broken down into simple sugars when consumed. These sugars are subsequently absorbed into the bloodstream.
Low carb diets have been shown in studies to effectively control type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Low-carb diets can help with blood sugar control, lowering medication needs and reducing the risk of diabetes complications. In fact, very-low-carb diets were considered standard treatments for diabetics before the discovery of insulin in 1921. People with type 2 diabetes were given a low-carb diet to follow for six months in one study. If they followed the diet, their diabetes was well controlled after more than three years. Similarly, throughout a four-year period, people with type 1 diabetes who followed a carb-restricted diet saw significant improvements in blood sugar levels. Counting carbohydrates is one method for reducing carb consumption.

Go low-carb 
Go low-carb -
Sugars and refined grains are examples of refined carbohydrates, also known as processed carbs. Table sugar, white bread, white rice, soda, candy, breakfast cereals, and desserts are all examples of refined carbohydrates.
Almost all nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and fiber have been eliminated from refined carbohydrates. Because refined carbohydrates are easily and quickly absorbed by the body, they are considered to have a high glycemic index. This causes blood sugar to rise. Major observational research of over 91,000 women discovered that a high-glycemic-index carbohydrate diet was linked to an increase in type 2 diabetes. After eating high-glycemic-index foods, you may experience a spike in blood sugar followed by a drop, which can promote hunger and lead to overeating and weight gain. Whole-grain foods, as well as most fruits, non-starchy vegetables, and legumes, have a lower glycemic index.

Eat fewer refined carbs 
Eat fewer refined carbs -
On a daily, the average American consumes 22 teaspoons (88 grams) of added sugar. This is around 350 calories. While some of it is added as table sugar, the majority of it is found in processed and prepared foods like candy, cookies, and sodas.
Sugars like sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup have no nutritional value. They're basically empty calories. These simple sugars are quickly broken down by your body, resulting in a rapid rise in blood sugar. Sugar consumption has been linked to the development of insulin resistance in studies. This occurs when the cells do not respond properly to the release of insulin, leading to the body's inability to effectively control blood sugar. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) modified the way foods must be labeled in the United States in 2016. Foods must now list the quantity of added sugars in grams and as a percentage of the daily maximum recommended consumption. Sugar substitutes are an alternative to completely eliminating sugar from your diet.

Reduce your sugar intake 
Reduce your sugar intake -
In the United States, two out of every three adults are considered overweight or obese. Being overweight or obese might make using insulin and controlling blood sugar levels more challenging. This can result in blood sugar rises and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes as a result.
Although the precise mechanism is unknown, there is plenty of evidence linking fat to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes development. On the other side, weight loss has been shown to improve blood sugar control. In one 12-week research, 35 obese people lost an average of 14.5 pounds (6.6 kg) while eating 1,600 calories per day. Their blood sugar levels dropped by an average of 14%. Weight loss was shown to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58% in another research on people without diabetes.

Keep a healthy weight 
Keep a healthy weight -
Exercise increases the sensitivity of your cells to the hormone insulin, which helps manage blood sugar spikes. Muscle cells take sugar from the blood during exercise, which helps to reduce blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar increases can be reduced by both high-intensity and moderate-intensity exercise. In one research, 27 people who exercised at a medium or high intensity showed similar improvements in blood sugar control. Blood sugar regulation may be affected by whether you exercise on an empty or full stomach. According to one research, exercising before breakfast lowers blood sugar levels more efficiently than exercising afterward. Increasing exercise also helps weight loss and efficiently prevents blood sugar spikes.

Exercise more 
Exercise more -
Fiber is your friend if you have diabetes or prediabetes since it helps in blood sugar control and weight management. It can also help you avoid heart disease and some cancers. Fiber does not cause a spike in blood sugar like other carbs since the body cannot absorb and break it down. This can help you stay within your blood sugar target range.
Fiber is made up of plant parts that your body is unable to digest. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber, in particular, can help in blood sugar stabilization. It dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance that helps in slowing glucose absorption in the gut. Rather than a spike, blood sugar levels increase and fall gradually. Fiber can also make you feel full, which can help you eat less. Soluble fiber may be found in the following foods: oatmeal, nuts, legumes, some fruits, such as apples, oranges, blueberries and many vegetables.

Eat more fiber 
Eat more fiber -
Blood sugar levels might rise if you don't drink enough water. Your body produces a hormone called vasopressin when you are dehydrated. This causes your kidneys to retain fluid and prevents your body from eliminating sugar in your urine. Furthermore, it causes your liver to release more sugar into your blood. Those who drank at least 34 ounces (approximately 1 liter) of water per day were 21% less likely to develop high blood sugar than those who drank 16 ounces (473 ml) or less per day, according to a study of 3,615 people. An increase in vasopressin in the blood was connected to an increase in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in a long-term study of 4,742 people in Sweden.
The amount of water you should drink is frequently disputed. It mostly depends on the individual. Always drink as soon as you feel thirsty, and increase your water intake in hot weather or when exercising. Stick to water instead of sugary juices or sodas, as the sugar can cause blood sugar to spike.

Drink more water 
Drink more water -
Many health benefits have been discovered for vinegar, particularly apple cider vinegar. Weight loss, cholesterol reduction, antibacterial properties, and blood sugar control have all been related to it. Several studies demonstrate that consuming vinegar improves sensitivity to insulin and lowers blood sugar spikes.
In one study, participants who had just eaten a meal containing 50 grams of carbohydrates had their blood sugar levels drop dramatically thanks to vinegar. The stronger the vinegar, the lower the blood sugar, according to the study. Another study looked at the impact of vinegar on blood sugar levels following carbohydrate consumption. It was shown that vinegar increased insulin sensitivity by 19 to 34%. Vinegar can also help lower a food's glycemic index, which can help prevent blood sugar increases.

Add vinegar into your diet 
Add vinegar into your diet -
Both chromium and magnesium have been shown to help decrease blood sugar spikes in studies. Chromium is a mineral found that your body needs in small amounts. It is supposed to improve insulin action. Encouraging cells to absorb sugar from the blood, might help manage blood sugar increases. 13 healthy men were given 75 grams of white bread with or without chromium added in short research. Following the meal, the addition of chromium resulted in a 20% drop in blood sugar. Broccoli, egg yolks, shellfish, tomatoes, and Brazil nuts are all good sources of chromium.
Another mineral that has been linked to blood sugar control is magnesium. In one study, half of the participants received a 600-mg magnesium supplement along with lifestyle advice, whereas the other half received only lifestyle advice. Insulin sensitivity improved in the magnesium supplemented group. Another study looked at the combined effects of chromium and magnesium intake on blood sugar levels. They discovered that taking both supplements together improved insulin sensitivity more than taking either supplement alone. Spinach, almonds, avocados, cashews, and peanuts are all good sources of magnesium.
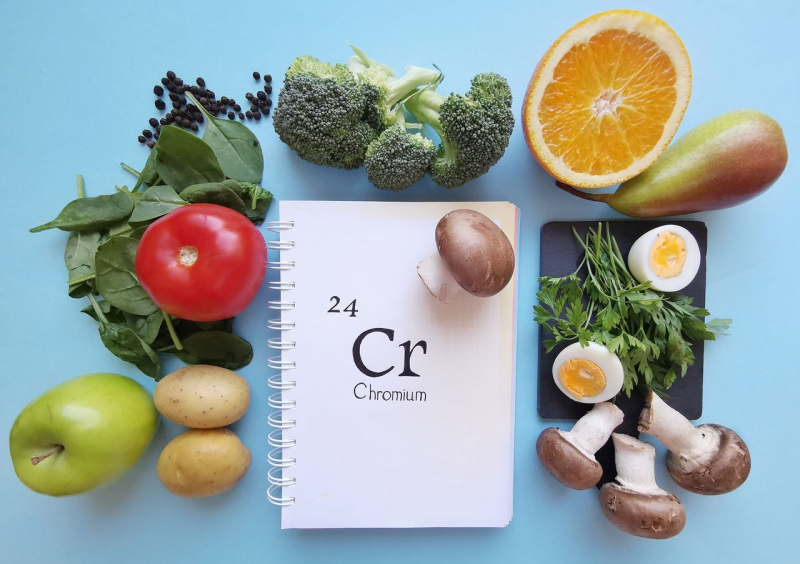
Get enough chromium and magnesium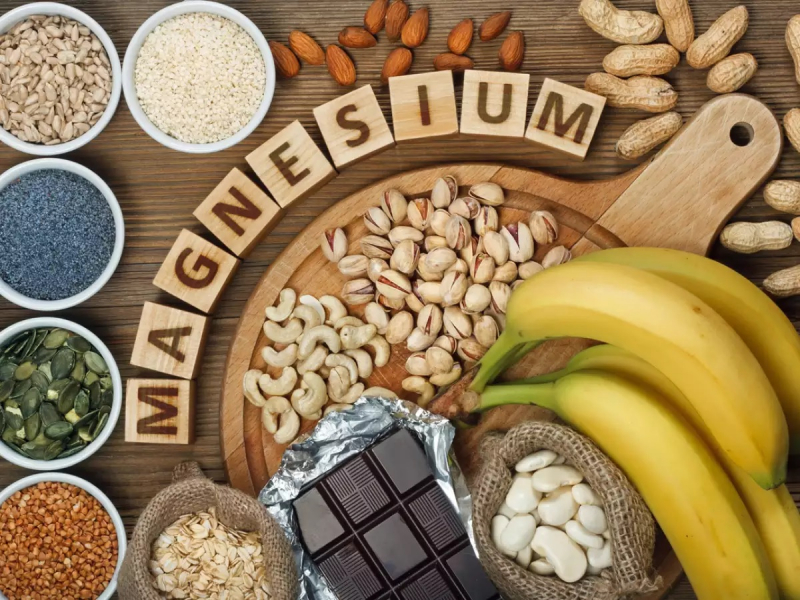 
Get enough chromium and magnesium -
For thousands of years, cinnamon and fenugreek have been used in alternative medicine. Both have been connected to blood sugar regulation. Cinnamon has been found to improve insulin sensitivity and minimize blood sugar increases after a carb-based meal in healthy people. One of these investigations followed 14 people who were in good health. When compared to eating the pudding alone, eating 6 grams of cinnamon with 300 grams of rice pudding dramatically lowered blood sugar spikes.
Fenugreek seeds are abundant in soluble fiber, which is one of their features. Reducing glucose digestion and absorption helps to reduce blood sugar spikes. Fenugreek significantly lowered blood sugar two hours after eating, according to a review of ten research. Fenugreek has been shown to help lower blood sugar spikes. Although it may be added to food, because of its strong flavor, some people prefer to take it as a supplement.
Add some spice to your diet 
Add some spice to your diet































