Top 9 Best Brain Foods for Kids
If you have children or are responsible for raising them, you undoubtedly want to make sure they eat well so they may live the healthiest lives possible. All ... read more...areas of health, including the development and operation of the brain, depend on proper nutrition. Every vitamin is crucial for healthy brain function. However, research has revealed that some nutrients and foods promote brain growth and enhance cognitive performance in children and adolescents. The best foods for kids' brains are discussed in this article.
-
One of the healthiest things you can consume is eggs. Thankfully, children adore them as well. Choline, vitamin B12, protein, selenium, and other elements that are essential for brain growth and cognitive function are abundant in eggs. The growth of the brain is particularly dependent on vitamin choline. Adding choline to a child's diet within the first 1,000 days of life may actually assist brain growth, protect against nerve cell damage, and enhance cognitive performance, according to a 2020 analysis of 54 research.
Furthermore, studies show that dietary patterns high in eggs and other nutritious foods, like legumes and fruit, are linked to lower IQ scores than dietary patterns high in sugary foods, such as cookies, and sweets. Choline demands for children and teenagers aged 9 to 13 are more than 75% met by two whole eggs, which have 294 grams of choline in total.

Eggs 
Eggs -
Anthocyanins, which are advantageous plant chemicals, are abundant in berries. Anthocyanins may provide a number of advantages for the health of the brain, according to scientists. They may have anti-inflammatory effects, improve blood flow to the brain, stimulate the growth of new nerve cells, and boost the expression of specific proteins. This contains BDNF, a neurotrophic factor that plays a role in memory and learning. Numerous research findings suggest that children's cognitive performance is favorably impacted by berry consumption.
For instance, a study of 14 kids aged 7 to 10 revealed that those who drank 200 grams of a blueberry beverage rich in flavonoids considerably outperformed those who drank a control beverage on a word memory test. Furthermore, studies show that children between the ages of 6 and 8 have worse cognitive performance when they consume fewer berries than other fruits and vegetables. In research with 2,432 teenage boys and girls, a high berry intake was also connected to superior academic achievement.

Berries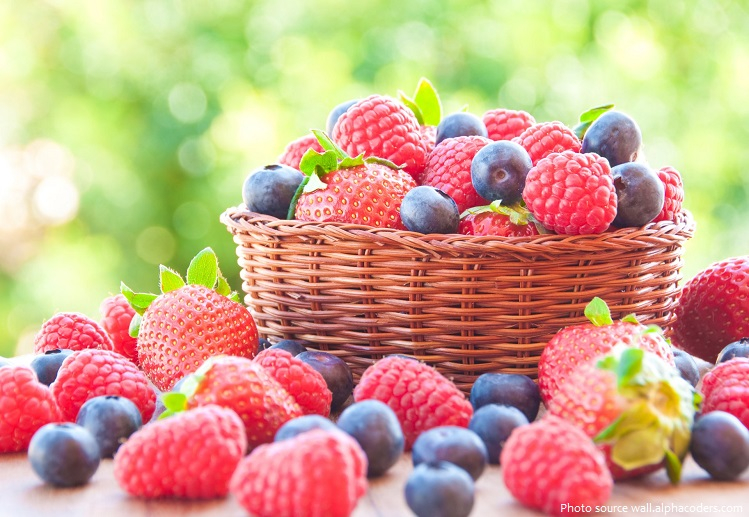 
Berries -
Omega-3 fatty acids, iodine, and zinc are just a few of the elements found in seafood that are very crucial for maintaining healthy brain function. For instance, the body needs zinc for the growth and development of nerve cells, but omega-3 fatty acids are essential for healthy brain function. Iodine is required by the body to make thyroid hormones, which are crucial for brain development. Numerous studies have linked seafood eating to improved cognitive performance in kids and teenagers. In fact, research has connected eating fish to children's increased academic performance and higher IQ scores.
Furthermore, children's cognitive development may be significantly impacted by low blood levels of omega-3 fats. However, because some forms of seafood are high in pollutants like mercury, eating too much fish may be detrimental to cognitive function, according to a study. Offer your youngster shellfish that has less mercury, such as clams, shrimp, salmon, trout, and herring, as a result.
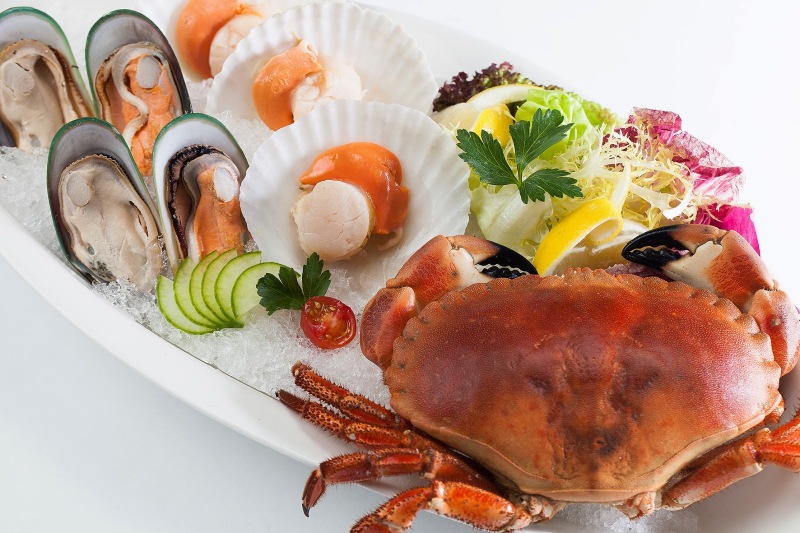

Seafood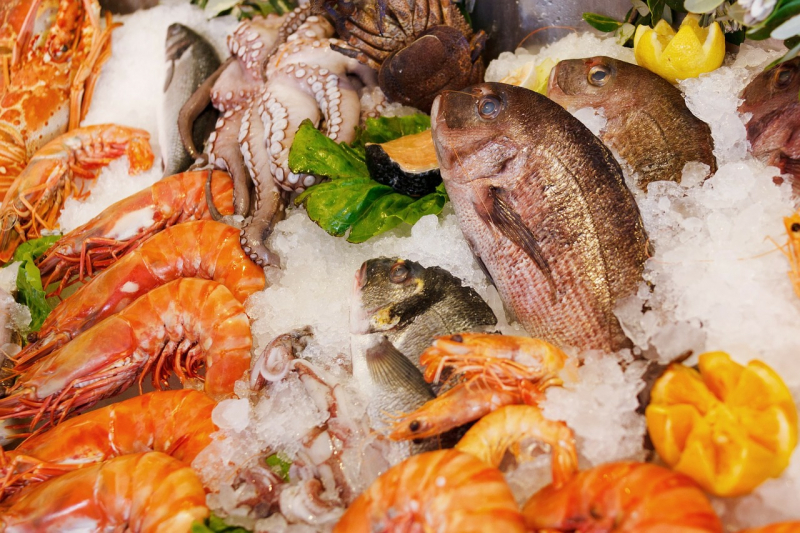 
Seafood -
Although it may be difficult to encourage your child to consume leafy greens, research indicates that these nutrient-rich veggies are crucial for children's brain development. There are substances that protect the brain in green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and lettuce, including folate, flavonoids, carotenoids, and vitamins E and K1. According to one study, youngsters who consumed enough folate had higher cognitive scores than those who did not. Additionally, studies indicate that a diet rich in foods containing carotenes, such as leafy greens, may improve a child's cognitive performance.
Leafy greens are high in carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin. These build up in the retina, a layer of your eye after you consume them. The amount of these pigments in the eye is gauged by something called macular pigment optical density, or MPOD. According to certain research, MPOD and children's cognitive development are favorably correlated.
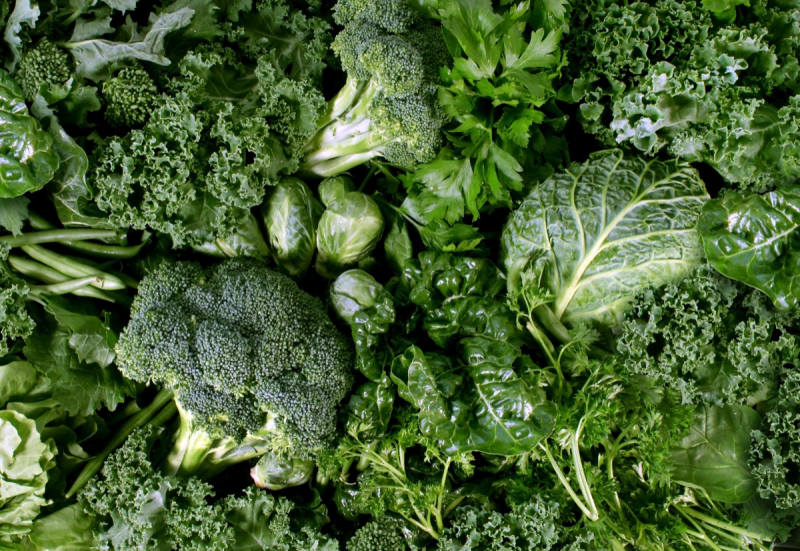

Green leafy vegetables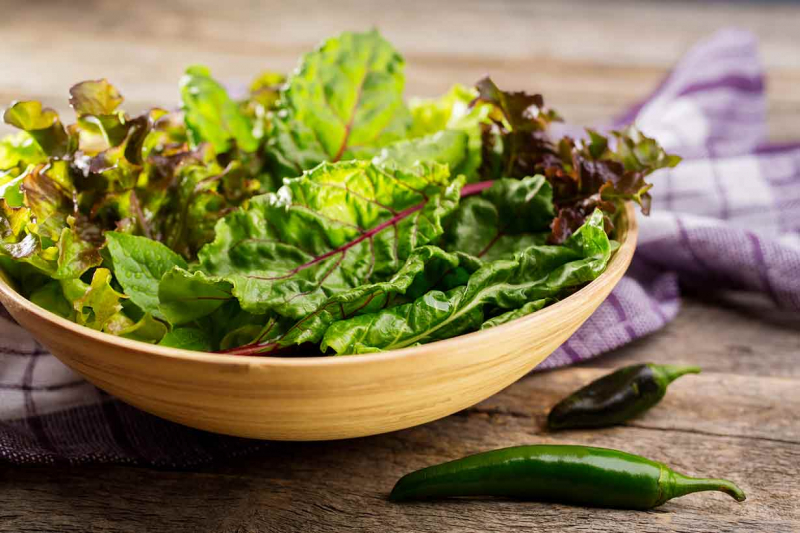 
Green leafy vegetables -
One of the most abundant food sources of flavonoid antioxidants, including epicatechin and catechin, is cocoa and cocoa derivatives like cacao nibs. Studies have revealed that these substances may be beneficial to the health of the brain since they contain anti-inflammatory and brain-protective characteristics. The brain receives more blood thanks to cocoa flavonoids, which also enhance visual processing. They help people perform better on specific cognitive tasks, according to research. Additionally, young people who consume cocoa may do better cognitively.
Both short- and long-term cocoa consumption improved cognitive function in children and young adults, according to a study of 11 research. The researchers hypothesized that consuming cocoa could improve cognitive function in linguistic learning and memory-related activities. However, further study has to be done on this by scientists.

Cocoa 
Cocoa -
Due to their sweet flavor, oranges are a popular citrus fruit and a kid's favorite. Your child's general health, including their cognitive health, may be enhanced by having oranges in their diet. Hesperidin and narirutin are only two of the many flavonoids found in oranges. Orange juice is really one of the most popular foods that contain flavonoids. Consuming foods and drinks high in flavonoids, such as oranges and orange juice, may assist increase blood flow to the brain and nerve activity, which may improve cognitive performance.
Vitamin C, a substance that is vital for the functioning of the brain, is also abundant in oranges. Vitamin C is essential for healthy brain growth, the generation of neurotransmitters, and other processes. Compared to adults with vitamin C insufficiency, studies show that individuals with adequate blood levels of vitamin C perform better on tasks requiring focus, working memory, attention, recall, decision speed, and recognition.
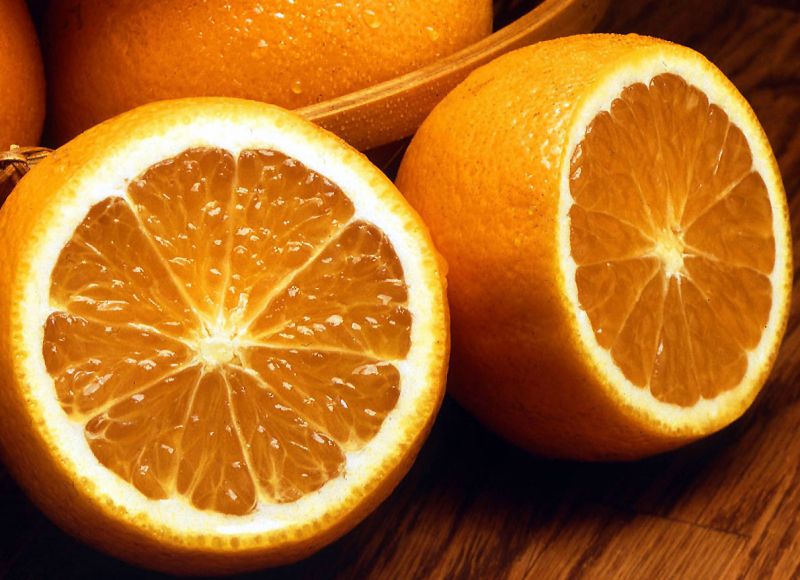

Oranges 
Oranges -
You may help your child's brain health by giving them unsweetened yogurt for breakfast or a protein-rich snack. Iodine, a vitamin required for brain growth and cognitive function, may be found in dairy products like yogurt. According to studies, kids with diets high in iodine are less likely to experience cognitive impairment than kids with diets low in iodine. Iodine deficiency is more prevalent in children and pregnant women, especially in underdeveloped countries, it is crucial to remember.
Yogurt has a lot of additional nutrients, such as protein, zinc, B12, and selenium, which are crucial for brain growth and function in addition to being a rich source of iodine. Additionally, research has shown that breakfast is crucial for kids' brain development. Because children's brains have a larger requirement for glucose than adults', regular meals that offer sustained energy are more crucial for kids than for adults. This implies that in order to promote energy levels and cognitive function, kids need to recharge with a nutritious meal in the morning. To promote your child's brain health, prepare a nutrient-dense breakfast that includes foods that are good for the brain. Serve them plain yogurt with berries, homemade granola, cacao nibs, and pumpkin seeds as a treat.

Yogurt 
Yogurt -
Around the world, iron deficiency is widespread, and children are especially susceptible. Children's academic performance and cognitive development may suffer from low iron status. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and iron insufficiency have both been linked (ADHD). The most vulnerable age group for iron deficiency is thought to be children under the age of 7. Make sure iron-rich foods are part of your child's diet to help avoid iron deficiency. Red meat, chicken, shellfish, beans, and spinach are a few of these.
Remember that heme iron, which is present in animal foods, is better absorbed by the body than non-heme iron, which is present in plant-based meals. The optimum diet for your child should include a variety of heme and non-heme iron sources. Non-heme iron-rich meals may benefit from the addition of vitamin C sources to increase absorption. Lemon juice, for instance, might be added to a spinach salad.

Iron-rich foods 
Iron-rich foods -
Nuts and seeds are extremely nutrient-dense foods that have been linked to increased cognitive performance. These include protein, iron, zinc, folate, vitamin E, and folate. Additionally, studies have demonstrated that consuming nuts can enhance the nutritional content of children's diets and increase their consumption of vital elements including fiber, protein, and healthy fats. Better academic achievement and cognitive function are related to diet quality.
317-child research discovered a correlation between consuming nuts and gains on the symbol digit modality exam (SDMT). In the 90-second SDMT, participants must match numbers with geometric shapes. This test is used by scientists to assess brain activity. According to studies, college-aged students who consume nuts show benefits in a few different areas of cognitive ability. Additionally, kid-friendly foods like nuts, seeds, and nut and seed butter can help increase the nutritious richness of meals and snacks.
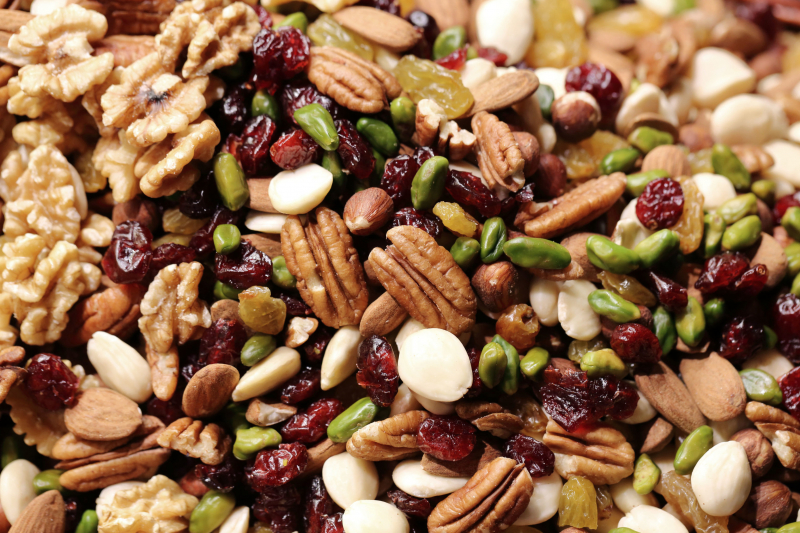

Nuts and seeds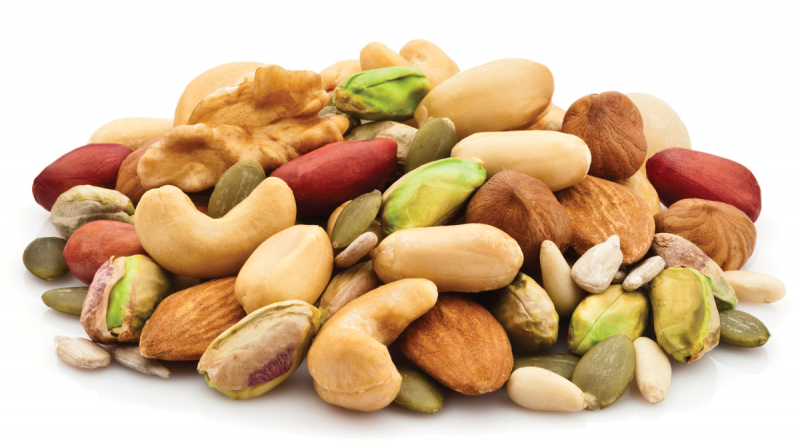 
Nuts and seeds