Top 5 Ways to Compress Large Audio Files
Reducing the size of large audio files is indeed a great way to conserve storage space and expedite file transfers. Nonetheless, it may seem challenging to ... read more...determine the best course of action. Toplist has compiled a list of top 5 Ways to Compress Large Audio Files. Check it out!
-
Converting audio files from uncompressed formats like WAV, AIFF, or FLAC to compressed formats like MP3 or AAC is indeed an effective way to reduce file size. These compressed formats utilize various encoding techniques to discard some audio data that is less perceptible to the human ear, resulting in a smaller file size.
Many audio editing software tools, including Audacity and Adobe Audition, offer the capability to convert audio files between different formats. This conversion process typically involves selecting the desired output format and adjusting specific settings such as bitrate and quality, depending on the software you are using.
It's worth noting that when converting to a lossy compressed format like MP3 or AAC, there will be some loss of audio quality due to the data compression. Therefore, it's important to choose an appropriate bitrate or quality level that balances file size reduction with acceptable audio quality for your specific needs.
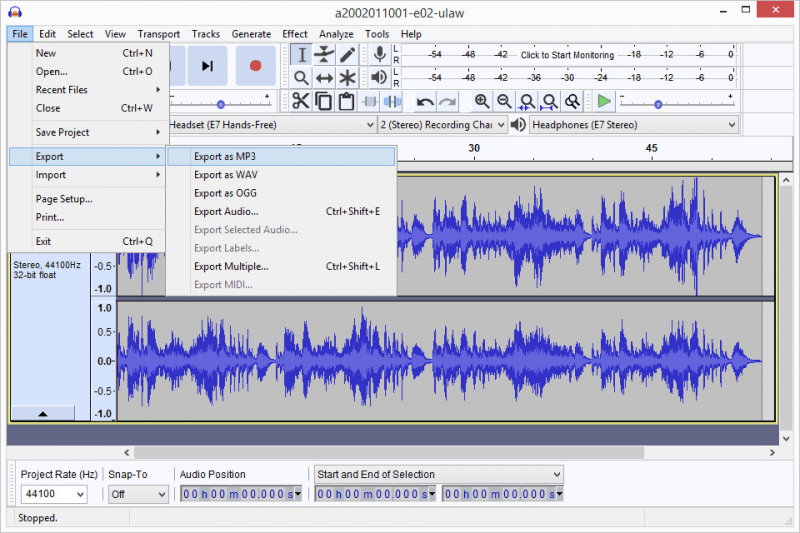
Photo via lifewire.com 
Photo via lifewire.com -
Adjusting the bitrate is indeed an effective way to compress audio files. By lowering the bitrate, you reduce the amount of data used to represent the audio, resulting in a smaller file size. However lower bitrates also lead to a decrease in audio quality.
When adjusting the bitrate, it's important to find a balance that suits your specific needs. Higher bitrates preserve more audio details and result in better quality but larger file sizes, while lower bitrates sacrifice some audio details to achieve smaller file sizes. The optimal bitrate will depend on factors such as the type of audio content, intended use, and available storage or bandwidth constraints.
It's worth noting that different audio formats and codecs may have specific bitrate options and limitations. For example, MP3 files typically offer a range of bitrates to choose from, while formats like AAC or Ogg Vorbis may provide additional options for more efficient compression.

Photo via dacast.com 
Photo via dacast.com -
Audio compression software allows you to choose between lossy and lossless compression methods. Lossy compression algorithms, like MP3 or AAC, discard some audio data to achieve smaller file sizes. Lossless compression algorithms, such as FLAC or ALAC, reduce file sizes without sacrificing any audio information. The choice between these methods depends on your priorities regarding file size and audio fidelity.
Most audio compression software allows you to adjust the bitrate or quality settings to control the trade-off between file size and audio quality. Higher bitrates or quality settings result in larger file sizes but better audio fidelity, while lower settings reduce file sizes but may introduce perceptible audio artifacts. The software provides a visual or numerical representation of the resulting file size, helping you make informed decisions.
If you have multiple audio files that need compression, audio compression software often supports batch processing. This feature allows you to compress multiple files simultaneously, saving time and effort. You can specify compression settings for the entire batch or set individual parameters for each file.
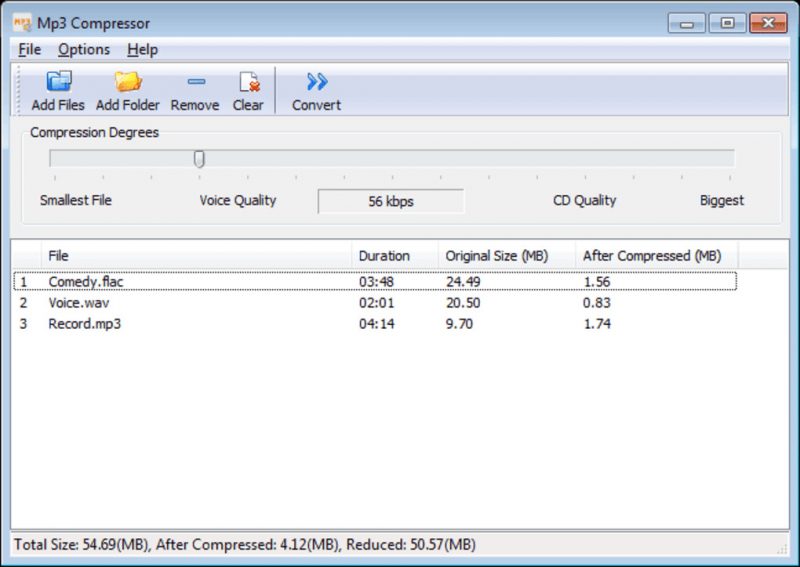
Photo via anymp4.com 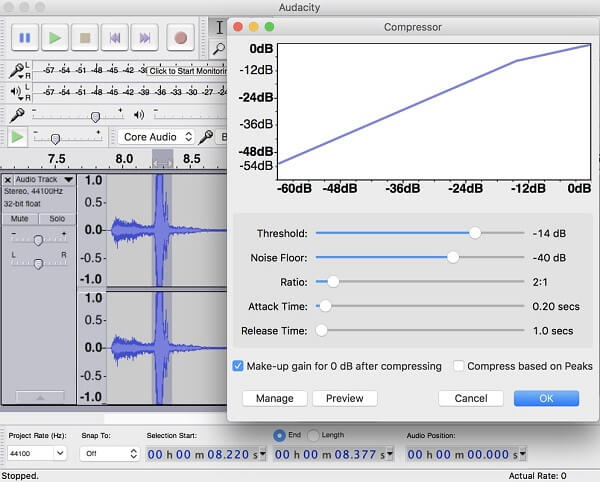
Photo via anymp4.com -
Removing unnecessary parts from audio files can help reduce their size without compromising the audio content. Utilize audio editing software such as Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand to trim or cut out unwanted sections of the audio. These software programs provide precise control over the editing process, allowing you to select and remove specific portions of the audio waveform.
Many audio editing tools have built-in features or plugins that can automatically detect and remove silent or low-volume sections of an audio file. This can be particularly useful for removing pauses, gaps, or background noise between spoken or musical segments.
If you have audio segments at the beginning or end of a file that you want to remove, consider using fade-in and fade-out effects. These effects gradually decrease the volume at the beginning or end of a selected region, creating a smooth transition and eliminating abrupt cuts.
When removing a section from the middle of an audio file, you can apply crossfading techniques to maintain a seamless transition between the remaining portions. Crossfading involves overlapping adjacent audio segments and gradually fading one out while fading the other in, ensuring a smooth transition without audible clicks or gaps.
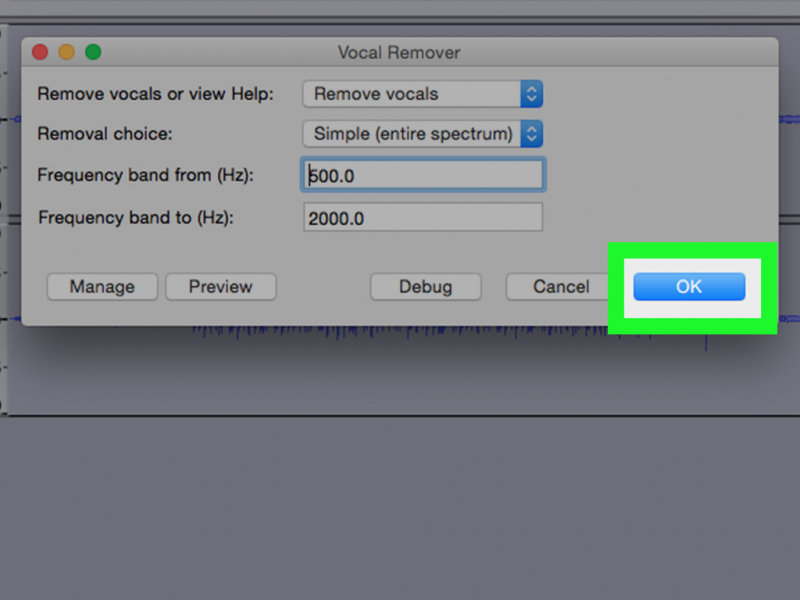
photo via wikihow.com JWildfong channel on youtube -
Splitting an audio file involves dividing it into smaller segments, which can be useful for various purposes such as creating excerpts, organizing content, or fitting file size limitations. Utilize audio editing software like Audacity, Adobe Audition, or GarageBand to split the audio file. These tools provide features that allow you to select specific portions of the audio and split it into separate files. You can typically set start and end points or use the software's waveform visualization to identify the desired segments.
Some audio formats, such as WAV or MP3, support embedded cue points, which are markers that indicate where an audio file should be split. You can use software that supports cue points to set markers at the desired split locations. Then, use the software's export or conversion feature to save each segment as an individual file.
If you prefer working with command-line tools or need to automate the splitting process, you can use audio manipulation libraries like FFmpeg or SoX. These tools provide command-line interfaces that allow you to specify the split points and export the resulting segments as separate files.
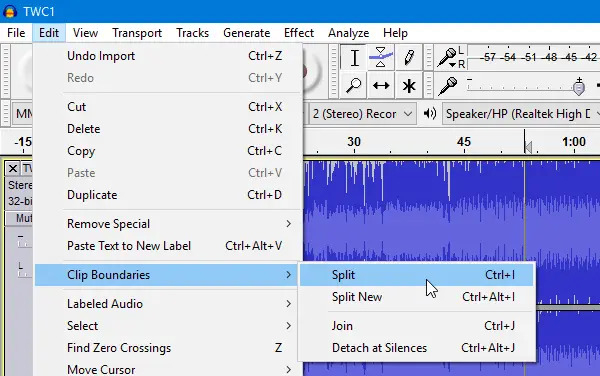
photo via musicianwave.com 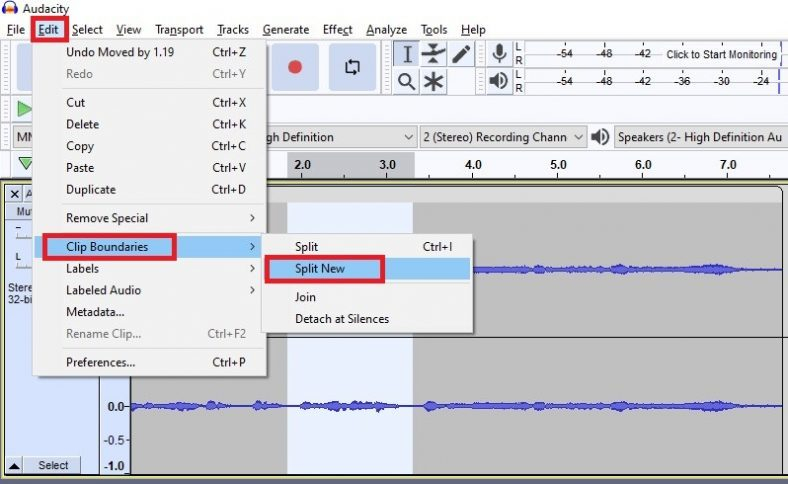
photo via musicianwave.com